One often comes across technical terms like edge and cloud computing. While the latter is still relatively well-known around the world, the former needs to be explained. This article highlights the basics of edge and cloud computing, their differences, and their relationship with one another. It also sheds light on the future of edge and cloud computing.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a distributed open-stage computing framework near the things or information sources at the system edge. It coordinates the abilities of systems, networks, and applications. By delivering edge-intelligent services, edge computing meets the critical requirements of industry digitalization, including credentialing services, by providing agile networks, real-time applications, data optimization, application intelligence, security, and privacy protection.
Edge computing is defined in a variety of ways by people of different fields and interests.
IBM defines edge computing as “a distributed computing framework that brings enterprise applications closer to data sources, such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices or local edge servers.”
Similarly, Hewlett Packard defines edge computing as “the practice of processing data near the edge of your network, where the data is being generated, instead of in a centralized data-processing warehouse.”
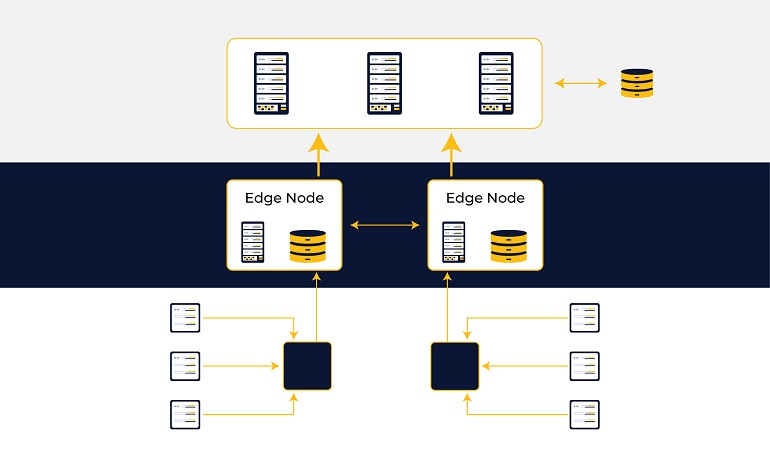
Edge computing brings calculation and information stockpiling nearer to the gadgets where it’s being accumulated, as opposed to depending on a focal area that can be hundreds of miles away. The computation and storing of gathered data over the edge of the node are known as edge computing. It connects the physical and digital worlds via smart devices, smart systems, smart assets, and smart services.
Advantages of Edge Computing
The primary benefit of edge computing is that it mitigates the risk of network breakdowns or cloud slowdowns when timely access to data is critical. Data utilization is very important in Edge Computing. Edge computing achieves this by embedding automation and intelligence into your physical devices.
Some of the other significant advantages of edge computing are:
Unprecedented Data Control
Edge computing gives you massive control over data as it is the first point where computing accesses data. You can determine which data you want to keep and which ones you want to route, summarize, or obfuscate. You can also add controls at this point to manage data privacy, reliability, and security.
Take the example of facial recognition technology in smartphones. It uses edge computing, meaning that AI retains your face’s image on your phone. This ensures your privacy and security are not compromised, which is possible when you move the same to cloud services.
Reduced Latency
Edge computing has low latency due to shorter network uptime, bandwidth limitations, and round-trip times.
Lower Costs
Processing your data at the edge makes your cloud upload and storage a lot cheaper. You don’t need full-fidelity data when you can make do with a summary or key insights.
What is Cloud Computing?
The cloud is basically the internet. Cloud computing also often comes with varying definitions depending upon who defines it and to which field one belongs. You come across many different definitions because IT companies, academics, industry specialists, and analysts define cloud computing as they deem fit. Such descriptions are usually aligned with their professional backgrounds. Cloud computing is all about running workloads within the cloud.
Cloud computing is a service provided to you by other companies which you can access using the internet. One can access hardware and software services just by connecting to the cloud service provider’s network. Here are some definitions of cloud computing:
According to the International Data Corporation (IDC), cloud computing is “an emerging IT development, deployment, and delivery model, enabling real-time delivery of products, services, and solutions over the Internet (i.e., enabling cloud services).”
The 451 Group defines cloud computing as “a service model that combines a general organizing principle for IT delivery, infrastructure components, an architectural approach, and an economic model – basically, a confluence of grid computing, virtualization, utility computing, hosting and software as a service (SaaS).”
Merrill, a leading American investment management company, defines cloud computing as “the idea of delivering personal (e.g., email, word processing, presentations) and business productivity applications (e.g., salesforce automation, customer service, accounting) from centralized servers.”
Cloud computing enables a user to edit, create, delete, publish, compute, and store data on a device like a computer, mobile device, or tablet through the Internet. A user can use the pre-installed applications on a server on any platform and at any time.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become an integral part of cloud computing. It enhances the overall efficiency of cloud-based services by leveraging machine learning and deep learning. In many use cases, cloud computing and AI have led to better management, increased revenues, and lower costs.
Here are some cloud computing facts for you.
- More than 90% of companies use cloud computing.
- 80% of enterprises use Amazon Web Services (AWS) as their primary cloud platform.
- Enterprises use 1427 distinct cloud services on average.
Difference Between Edge Computing and Cloud Computing
The relationship between Edge and cloud computing is synergistic. While Edge computing deals with data processing in close vicinity to its source, cloud computing centralizes the data processing typically away or remotely. To further discuss the relationship between the two, we will highlight their differences to give the readers a better perspective.
The primary difference between the two is that while edge computing moves computing to the edge of the network and as close to data sources as possible, cloud computing generates and collects data from multiple locations and stores it in the cloud. Moreover, edge computing processes time-sensitive data quite efficiently. Whereas cloud computing is used to process non-time sensitive or non-time triggered data. Cloud computing (FaaS) is, by its very nature, a centralized process. This is what enables it to process data at scale very easily and efficiently, costing you a lot less.
Most companies store and process their data on the cloud since it has almost unlimited resources compared to the small and resource-constrained devices onsite. Storage and computing have been expanding at a much faster rate than the capacity of the network. No matter the size or volume of the data, cloud computing can handle it once it moves to the cloud.
But sometimes, you cannot or do not need to send your precious data to the cloud for processing. These include:
- Your internet connection is unstable or not working at all.
- You cannot transfer data offsite due to privacy regulations or security concerns.
- Your device needs to analyze data and make lightning-quick decisions.
The Future of Edge Computing and Cloud Computing
Although edge computing provides fantastic benefits, it will not overtake cloud computing. Edge computing handles, manages, and stores data locally. In fact, both will go hand in hand to enable efficient, secure, and scalable business processes.
Integrating a secure SDLC approach is crucial to ensuring that the development of edge and cloud-based applications is secure from the ground up, which complements the need for robust security measures in distributed computing environments.
Edge computing has certain limitations. For one, it leads to resource limitations on batteries, storage, bandwidth, and computing power. Edge computing is a key component of the cloud computing continuum. However, Some experts suggest that we should consider edge and cloud as integral parts of a computing continuum, where the cloud retains the central position in a network while the edge complements it from the “edges” of a network, so to speak.
Xavor Corporation can help you on your way forward to a promising future for both computing frameworks. Cloud services are already on the rise, as mentioned earlier. You can add edge computing to your cloud solutions to efficiently handle and optimize your enterprise applications. Cloud computing offers data analytics and new applications that are distributed to your edge computing network, which returns the data to the cloud with further feedback.
It’s a virtuous loop. Keep your business growing by combining and utilizing both technologies to offer highly personalized and contextualized experiences.
If you want any assistance with cloud computing models, Azure DevOps automated deployment, or services, contact us at [email protected].
FAQs
Q: What describes the relationship between edge computing and cloud computing in Accenture?
Ans: Accenture often combines edge and cloud computing to create hybrid solutions, optimizing data processing and storage for various client needs.
Q: What describes the relationship between edge computing and cloud computing cloud computing originally began as an?
Ans: Cloud computing originally began as a centralized data processing model, whereas edge computing is a decentralized approach, enabling data processing closer to the data source.
Q: How are edge and cloud computing similar?
Ans: Both edge and cloud computing involve data processing and storage, but they differ in their proximity to data sources. Edge computing is closer to the data source, while cloud computing is centralized.
Q: What describes the relationship between 5G edge computing and cloud computing?
Ans: 5G enhances both edge and cloud computing by providing high-speed, low-latency connectivity. Edge computing leverages 5G for real-time data processing, while cloud computing may use 5G for faster data transfer and access.












