There is no industry that hasn’t been touched by AI. Healthcare and life sciences are also at a crucial juncture, probably the most important one since the introduction of modern medicine. AI in healthcare can totally change one of the essential facilities for humans for the better. AI and digital technologies are reshaping our treatments, diagnoses, and caregiving methods. And this transformation is much needed because healthcare systems around the world are currently stretched beyond their capacity.
Healthcare is not new to digitization. But AI solutions in healthcare bring intelligence that regular automation tools don’t bring to the table. Imagine someone’s life is saved because an intelligent AI agent detected an anomaly in their health through data before any symptoms appear. That’s right, applications of AI in healthcare treat every data point, every statistic as a signal to improve patient outcomes that humans may miss.
In this blog, we will elaborate in detail how is AI used in healthcare, its benefits, real-world use cases, and key future trends in 2026. And there are always two sides to a coin; therefore, we will also tackle the pressing challenges of AI in healthcare and what the way forward is.
How is AI used in healthcare?
So, first things first: how do they actually use AI in healthcare settings? If you’re thinking that doctors just ask ChatGPT for clinical help, it’s not that simple, but you are on the right track. AI in the medical field helps healthcare workers in their daily operations. It is as much about making the work of healthcare workers easy as it is about improving patient outcomes.
Let’s look at some of the ways AI is used in the healthcare industry.
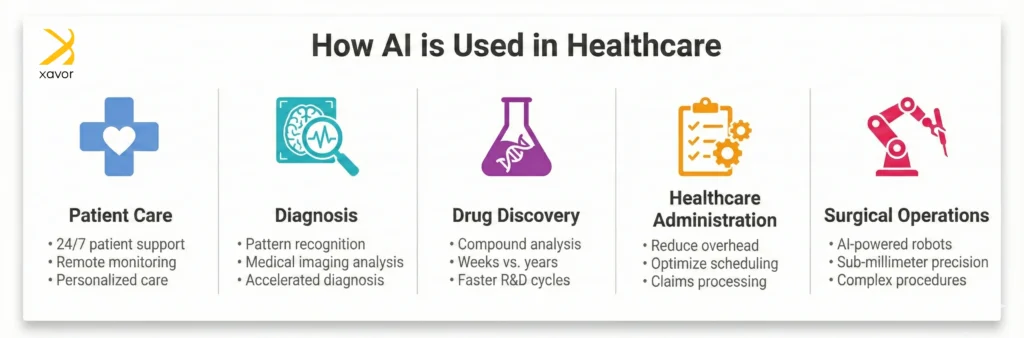
1. Patient care
When people talk about AI in healthcare, patient care is where its impact becomes most tangible. It is used to provide always-on patient support, personalized care, remote monitoring, and much more.
2. Diagnosis
AI is particularly strong at diagnostic tasks that depend on pattern recognition, especially in medical imaging and signals. These systems don’t “understand” disease the way clinicians do. However, they learn statistical patterns from large datasets and apply them consistently to provide accelerated diagnosis.
3. Drug discovery
Paracetamol was first synthesized in a laboratory in 1878, but it only became commercially available under the trade name Panadol in 1955. Drug discovery is a long, expensive process. AI in healthcare speeds up this process by analyzing and identifying promising compounds in weeks rather than years.
4. Healthcare administration
One of AI’s biggest impacts on healthcare is also the least visible. Running a large hospital is really complex, with thousands of backend operations that people don’t see. Applications of AI in healthcare reduce administrative overhead, which directly affects care quality.
5. Surgical operations
This is where AI and robotics in healthcare can significantly improve outcomes. AI-powered surgical robots can assist surgeons in performing the most intricate, critical operations that might not be possible with human hand-eye coordination.
Benefits of AI in healthcare
The benefits of AI in healthcare are so profound and vast that the industry simply can’t keep it out of the scene.
These are some of the ways AI in healthcare makes the whole caregiving experience better for everyone.
1. Reduced clinician burnout
Working in the healthcare field isn’t for everyone. It is a high-stress domain with long shifts and constant pressure. Doctors, nurses, and paramedical staff are always on their toes. Moreover, studies consistently show that clinicians spend roughly a quarter to a third of their time on documentation and non-clinical tasks.
Combined with patient-facing tasks, this workload is mentally and physically taxing for them, which can burn out many healthcare professionals.
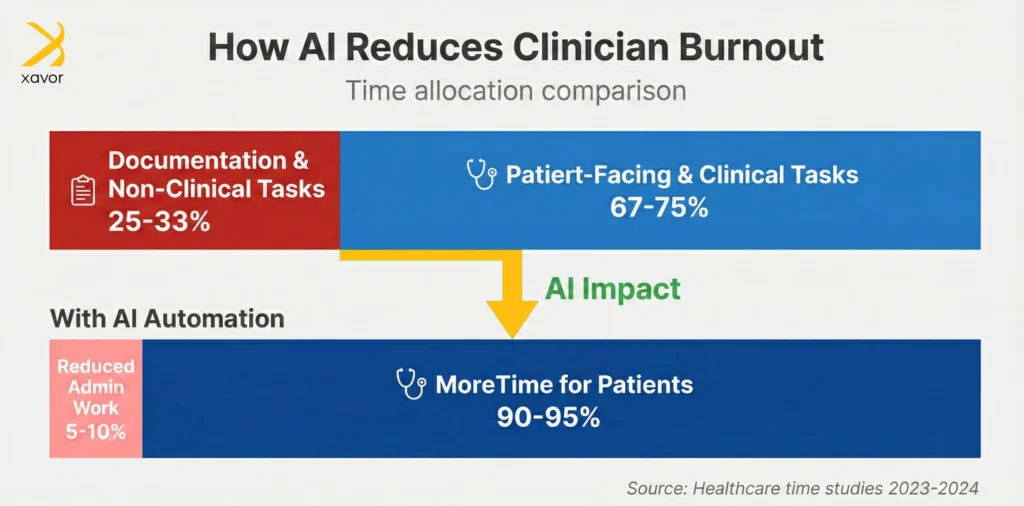
AI in healthcare helps take much of this burden off their shoulders. Applications of AI in healthcare do this by:
- Automating clinical notes
- Summarizing patient histories
- Assisting with monitoring and billing
Burnout contributes to medical errors, staff shortages, and rising costs. AI helps reduce this cognitive overload, which directly improves care quality.
2. Lower operational costs
You have people in the United States driving all the way to Canada because they can’t afford basic healthcare facilities back at home. However, it isn’t just because of expensive treatment; rather, there is a lot of inefficiency in traditional healthcare systems.
For example, in 2023, a patient in Massachusetts had to pay $1,677.51 after having a routine mammogram and sonogram. She was quoted $359 originally, which she paid. But the hospital struck her with a jaw-dropping bill weeks later because the estimate wasn’t binding due to the “complexity of healthcare billing.”
AI solutions in healthcare are designed to remove even small inefficiencies before they accumulate to cause patients any discomfort, like in the case of a crushing medical bill. Hospitals can partner with AI services in healthcare to improve:
- Scheduling optimization
- Patient flow management
- Claims processing and fraud detection
- Supply chain forecasting
Applications of AI in healthcare can save millions of dollars annually that are sapped by operational inefficiencies. It will make healthcare affordable for everyone and not just a privileged part of society.
3. Healthcare availability at scale
There is a chronic staffing crisis in the global healthcare system. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends one physician per 1,000 people. But in developing countries, that ratio is skewed with figures like 1:1300 or even worse.

Developed countries also have their own healthcare worker shortages because of an ageing population. Currently, the National Health Service (NHS) in the UK has over 40K vacant nursing posts, according to rough estimates. In Italy, there are now whole towns filled with the elderly as the country’s birth rate is at an all-time low. Stopgap solutions like immigration to fill the worker shortage in the healthcare systems in such countries are not viable in the long run.
AI in healthcare is the only long-term fix to scale healthcare services with the rising demand. For example, conversational AI in healthcare makes the whole process asynchronous and parallel. Using virtual assistants, a clinician can support thousands of patients instantly and without fatigue.
AI triage chatbots are also good examples of AI in healthcare. Such solutions can be used to:
- Collect symptoms in a structured form
- Ask follow-up questions dynamically
- Route patients to the right level of care
This is especially important for remote and underserved populations, where access is limited not by demand, but by availability.
4. Better outcomes and preventive care
Traditional healthcare setups prioritize quantity over the quality of the services provided because that is where their bread and butter is. As long as a patient keeps coming for tests and scans, it is profitable for healthcare organizations.
Recent advances in healthcare demonstrate how rapidly the shift toward value-based, data-driven care is accelerating. The future of AI in healthcare is linked to value-based models. Providers under this system are rewarded for:
- Preventing complications
- Reducing readmissions
- Managing chronic disease effectively
- Keeping patients healthy outside the hospital
All of this leads to better patient outcomes and experiences and keeps the population overall healthy.
5. Data integration in fragmented systems
The Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital in Florida has more than 150 terabytes of pediatric vital signs data. And these kinds of numbers are nothing out of the ordinary for large-scale hospitals and healthcare institutions. But that data is often scattered across different systems, which don’t integrate very well or at all.
So, imagine a scenario with a type 2 diabetes patient. The EHRs record their past admissions and HbA1c results from clinic visits, while the hospital lab system holds the blood glucose and kidney function tests. Meanwhile, the patient wears a wearable glucose monitoring device that tracks daily blood sugar fluctuations, meals, exercise, and sleep cycles. The doctor needs to know each and every one of these things for diagnosis.
Now, consider how AI innovations in healthcare make this process smooth and easy. Instead of replacing existing individual software, AI pulls data from multiple sources, cleans it, and turns it into a single, usable view of the patient. It can link past diagnoses, test results, medications, and recent vitals into one coherent timeline.
Real-world AI use cases in healthcare
In this section, we will dive deep into understanding some real-world AI use cases in healthcare, including all their technical details and minutiae.
1. Moorsfield Eye Hospital: AI preventing blindness
There is an Islamic saying that if God takes someone’s eyesight, then there is no compensation for them except paradise. It is a very powerful quote to think about it. The loss of touch, smell, or hearing can be partially compensated through other senses. But blindness deprives a person of reality in a way that’s difficult to reconstruct through other senses alone.
A serious eye condition called age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is one of the leading causes of blindness worldwide. Moorfields Eye Hospital in London is one of the world’s oldest specialist eye hospitals, active since 1805. Clinicians there review thousands of OCT scans to treat patients with AMD every week.
There are two forms of AMD:
- Dry AMD is more common in older adults and usually causes mild vision loss
- Wet AMD is less common but far more serious, often leading to permanent blindness
About 15% of patients with dry AMD eventually develop wet AMD. The problem is that this progression is hard to predict. OCT scans are highly detailed 3D images of the back of the eye. Reading them manually is time-consuming, and delays can mean slower disease detection.
Earlier research showed that AI could already help doctors analyze these scans faster and spot existing signs of wet AMD that need urgent treatment. So, in 2018, Moorfields partnered with Google DeepMind to develop an AI system that could help clinicians interpret OCT scans more efficiently.
The key technologies used in this example of AI in healthcare are:
- Advanced deep learning models to analyze OCT images pixel by pixel
- Cloud computing for large datasets and high computational power
- Image segmentation models to identify and separate retinal layers
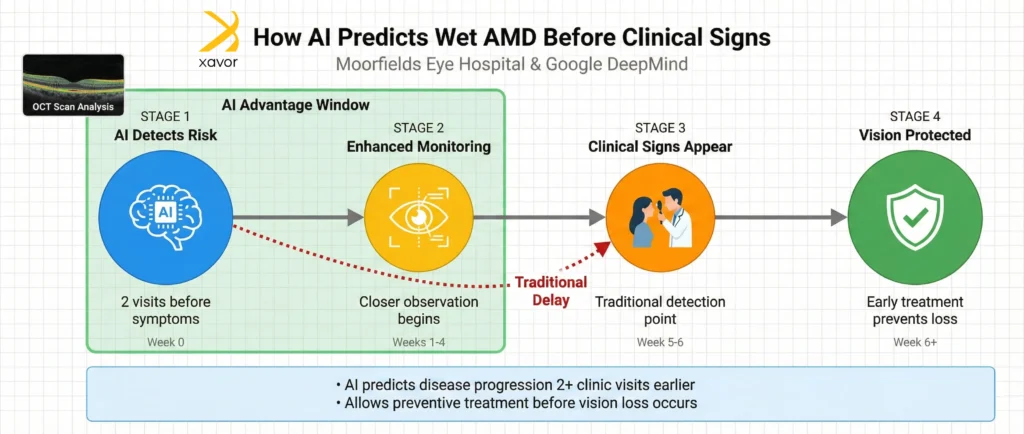
Using these AI solutions in healthcare, the model learned which changes usually appear before wet AMD develops.
As a result, the AI was able to predict that an eye was likely to worsen at least two clinic visits before clear clinical signs of wet AMD became visible. In practical terms, this means doctors could be warned earlier, monitor patients more closely, and start treatment sooner, which could potentially prevent serious vision loss.
2. OSF HealthCare: AI assistant
OSF Healthcare is a non-profit integrated healthcare platform in the United States. Their staff and call centers were inundated with overwhelming questions from patients, but the system for getting answers was fragmented. People often had to wait for hours or navigate complex websites just to figure out what to do next.
To resolve this matter, OSF Healthcare partnered with AI services in healthcare to implement a healthcare-focused AI virtual assistant designed for navigation and decision support on their website. It is a good example of conversational AI solutions in healthcare, which uses natural language processing (NLP).
Instead of calling or searching through multiple pages, patients can interact with the AI assistant to:
- Check symptoms
- Schedule appointments
- Choose caregiving delivery method
- Find answers to clinical and other questions
Moreover, the AI assistant is available 24/7, including nights and weekends, when call centers are typically unavailable.
OSF reports that 1 in 10 patients now interact with the AI assistant during their care journey, which is enough to say that patients are actually finding value in the solution.
3. Sanofi: Expedite drug discovery
Sanofi is a global pharmaceutical company focused on R&D-driven biopharma. It develops medicines and vaccines for various conditions like cancer, diabetes, immunology, neurology, and other rare diseases. To improve both patient outcomes and internal efficiency, Sanofi has applied AI across the entire drug lifecycle.
Drug discovery is slow and expensive. Finding a molecule that works and is safe to use can take years. On top of that, some important disease targets were traditionally considered “undruggable” because they are difficult to target with conventional methods. Sanofi, with the ambition to change that, partnered with a biotech company for AI-first drug discovery.
The core AI solutions in healthcare used in this case study are:
- Deep learning models trained on biological and omics data
- Graph neural networks (GNNs) to model molecular structures
- Generative AI in healthcare designs models to create novel drug molecules
- Bioinformatics pipelines to integrate multi-omics data
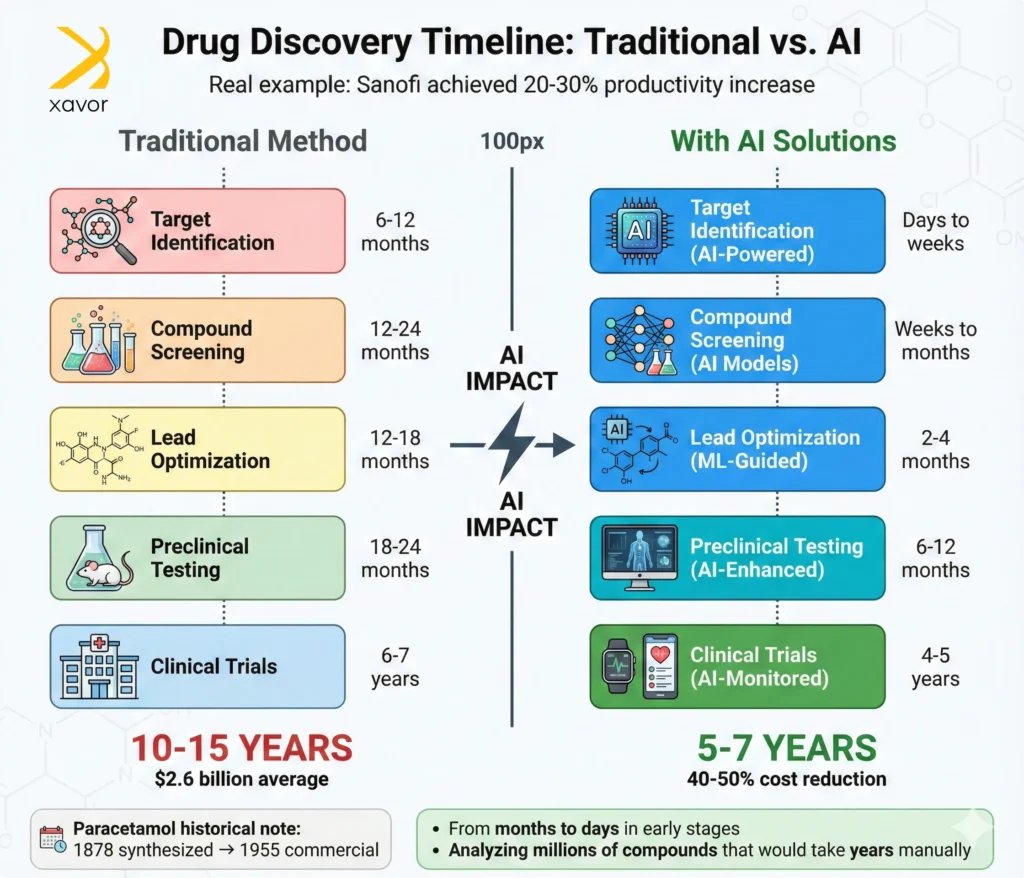
Using AI in healthcare allowed Sanofi to analyze massive biological datasets, which basically tells proteins that are most relevant to a disease. Narrowing millions of possibilities down to a small number worth testing in the lab shortened research cycles from months to days, and increased drug discovery productivity by 20–30%.
4. Cleveland Clinic: AI-assisted robotic surgery
Cleveland Clinic is one of the world’s leading academic medical centers and among the earliest and largest adopters of robotic surgery. It has performed tens of thousands of robot-assisted surgeries using a sophisticated robotic platform.
The healthcare organization deployed the robotic surgery platform across multiple departments. Surgeons’ hand movements are captured at the console and translated into much smaller, more precise movements by robotic arms, which allows surgeons to operate with sub-millimeter precision.
Furthermore, the system provides a magnified, 3D, high-definition view of the surgical field using computer vision. Real-time image processing enhances contrast and depth perception. As a result, surgeons see anatomy more clearly than with the naked eye or standard laparoscopy.
Robotics is really one of the fascinating applications of AI in healthcare. The level of precision and human-machine interaction in robotic surgery is a piece of art.
5. NaviGait: AI-powered dementia care
NaviGait is a spin-off by Xavor that builds AI-powered robotics for elderly care, especially for patients with dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. In just the start of this year, we saw the tragic deaths of Hollywood legend Gene Hackman, who was suffering from late-stage dementia, and his wife, Betsy. Unfortunately, such grim stories are now not that uncommon.
Our aim with NaviGait is to prevent such situations from happening. Navi is an AI-enabled healthcare robot developed by NaviGait, which uses AI and robotics to improve patient care, especially for older adults and those with cognitive or mobility challenges.
The robot is designed as a social companion and assistive robot, equipped with AI-driven perception, navigation, and interaction capabilities. It uses technologies, such as:
- ROS/ROS2 operating system
- Gait and movement analysis
- Edge AI inference
- Latest speech-to-text (STT) softwares and text-to-speech (TTS) models
Navi follows and engages patients, assists with reminders, tracks emotional and movement patterns, and provides companionship. It does so while keeping caregivers informed of changes in well-being.
The goal is to reduce caregiver burden, detect early health issues, and enhance quality of life for seniors.
Future of AI in healthcare: Key trends in 2026
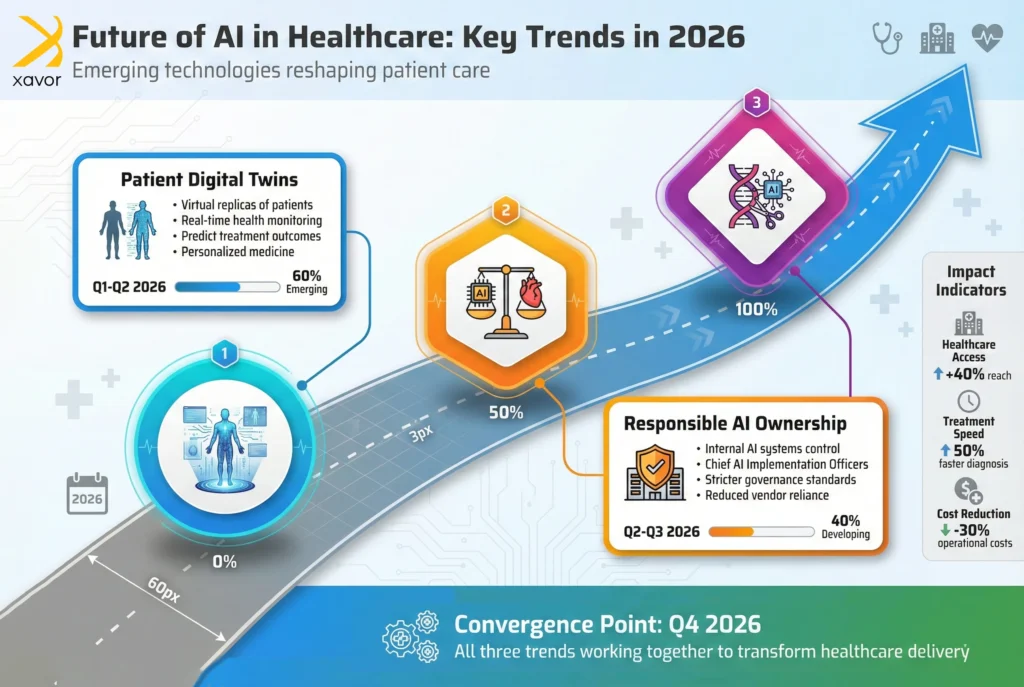
What does the future hold for AI in healthcare? Maybe a clairvoyant or a fortune cookie can tell the exact answer. However, the great thing about science is that it can also make great predictions without the vague, serendipitous style of psychics or ancient wisdom.
Based on industry trends and data, here are some emerging trends of AI in healthcare that might change the heart of the industry.
1. Patient digital twins with AI
It might sound a bit dystopian because when you talk about creating “twins” of a patient, people seem to think of something like cloning. But digital twins in healthcare are totally different, and much closer than you might think. A digital twin is a virtual, real-time replica of a physical entity. Digital twins are already used in manufacturing, engineering, and other fields.
But now, AI in the medical field is bringing this technology to healthcare providers. A human digital twin is a living digital model of a person’s body, built using AI and real-time data. It mirrors how a patient’s body behaves and changes over time.
Using wearable devices, it collects data and uses ML models to understand how the patient’s body works and how it reacts to disease or treatment.

If implemented properly, patient digital twins can enter healthcare into a completely different era. Human digital twins can move healthcare from trial-and-error to prediction and precision. And that’s just the start, it can make the work of healthcare professionals simple and safe, such as:
- Doctors can personalize treatments by testing therapies virtually.
- Surgeons can rehearse complex procedures on a patient’s digital anatomy to reduce risk.
- Clinicians can monitor patients remotely to catch problems early using wearable data.
In research, digital twins can accelerate drug discovery and clinical trials by simulating drug and immune responses before human testing. Lastly, in medical education, students may no longer have to cut open poor frogs to learn the anatomy of the human body. They can practice procedures safely on realistic, virtual patients.
2. Responsible ownership of AI in healthcare
As of now, many healthcare companies use third-party partners, such as subsidiaries or AI services in healthcare, to build or run their AI systems. There are some obvious reasons for that, like you don’t expect a hospital to have a team of AI experts and data scientists. However, circumstances demand that this approach has to change going into 2026.
Applications of AI in healthcare will only increase, and if something goes wrong, for example:
- Patient data is mishandled
- An AI system makes unsafe or biased decisions
- Rules or regulations are broken
Who will then take responsibility? No matter if it’s the third party who made the error, it is the hospital or the healthcare organization that has to answer for it. Patients put their trust in the hospital, not some AI lab working in the background. For healthcare organizations, it could cause irreparable reputational damage.
Therefore, we predict that for AI in healthcare to become truly integrated, hospitals will have to reduce their reliance on external vendors and focus on:
- Owning more of their AI systems internally, including data, models, and decision logic.
- New roles like Chief AI Implementation Officer (CAIO) in healthcare settings to oversee AI solutions in healthcare.
- Stricter governance and accountability, with clearer responsibility for AI outcomes.
- Fewer but more tightly controlled partners, chosen for transparency and compliance.
- Built-in risk, ethics, and compliance checks from the start.
3. AI-powered gene editing
Humans have been crossbreeding animals and plants for eons by adding new genes to make them more productive or disease-resistant. But gene editing does more than just add genetic traits. It makes precise changes to the very DNA of things, which wasn’t possible until CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) appeared on the scene.
Yes, there is much debate around the ethics of gene editing and whether it can be done safely. We leave the ethical aspect of it to your discretion, but here we want to talk about AI solutions in healthcare that can assuage its safety concerns.
CRISPR is a revolutionary biotechnology that allows scientists to cut and modify DNA at specific locations. The tech itself is powerful but very unpredictable. While it can precisely cut DNA to delete or insert genes, outcomes often vary from cell to cell, and off-target edits can introduce errors. And this isn’t just introducing errors in a computer code that you can fix later through software testing services. A faulty DNA “edit” in CRISPR could, at worst, cause:
- Cancer
- Harmful immune reactions
- Breakdown of critical biological functions
- Passing down genetic errors to future generations
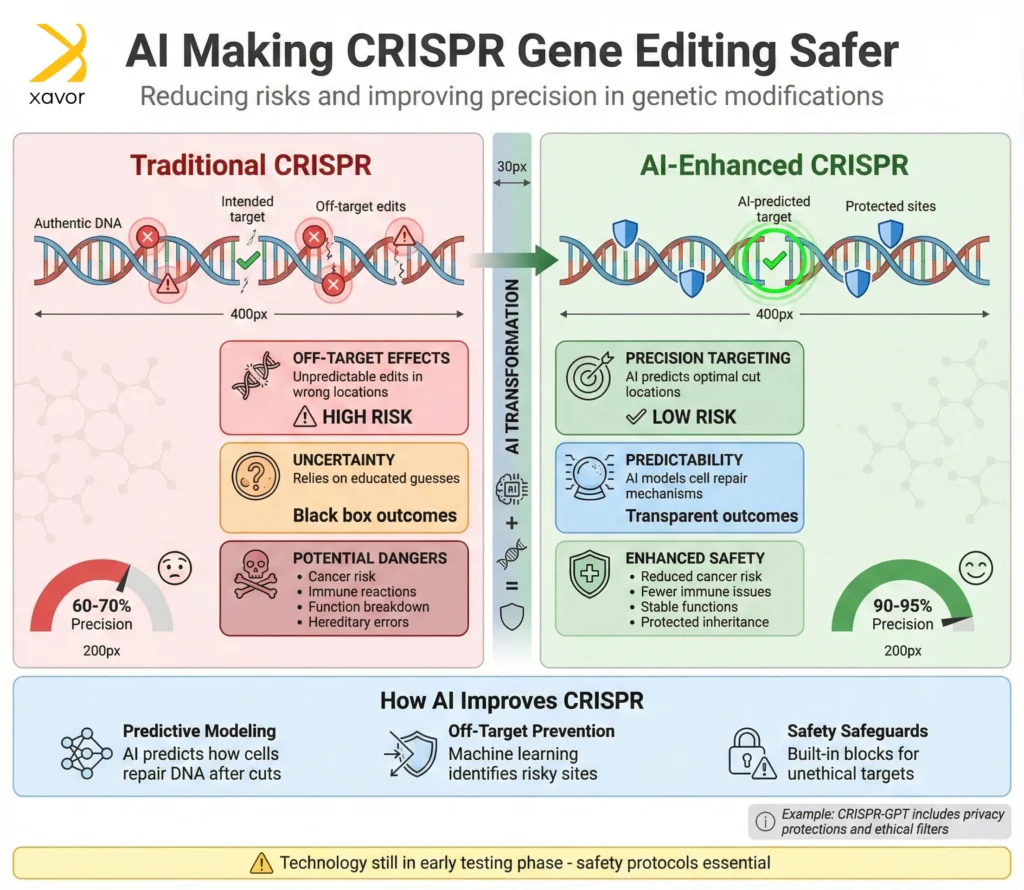
So, the safety concerns are legit and too dangerous to ignore. What makes it worse is that researchers have traditionally had to rely on educated guesses, which makes CRISPR feel like a black box.
AI in healthcare can help open that black box. An AI model is already under testing to predict how cells will repair DNA after a CRISPR cut, which can allow scientists to design edits that work with the cell’s natural repair process rather than against it. Moreover, agentic AI solutions in healthcare can significantly reduce off-target effects in early tests.
That said, these AI solutions in healthcare are still inchoate. Scientists are aware of risks like AI hallucinations and misuse, so systems like CRISPR-GPT include safeguards to block ethically sensitive targets and keep genetic data private. But if things remain on the right track, AI in healthcare will definitely make CRISPR safer and more predictable.
Major challenges of AI in healthcare in 2026
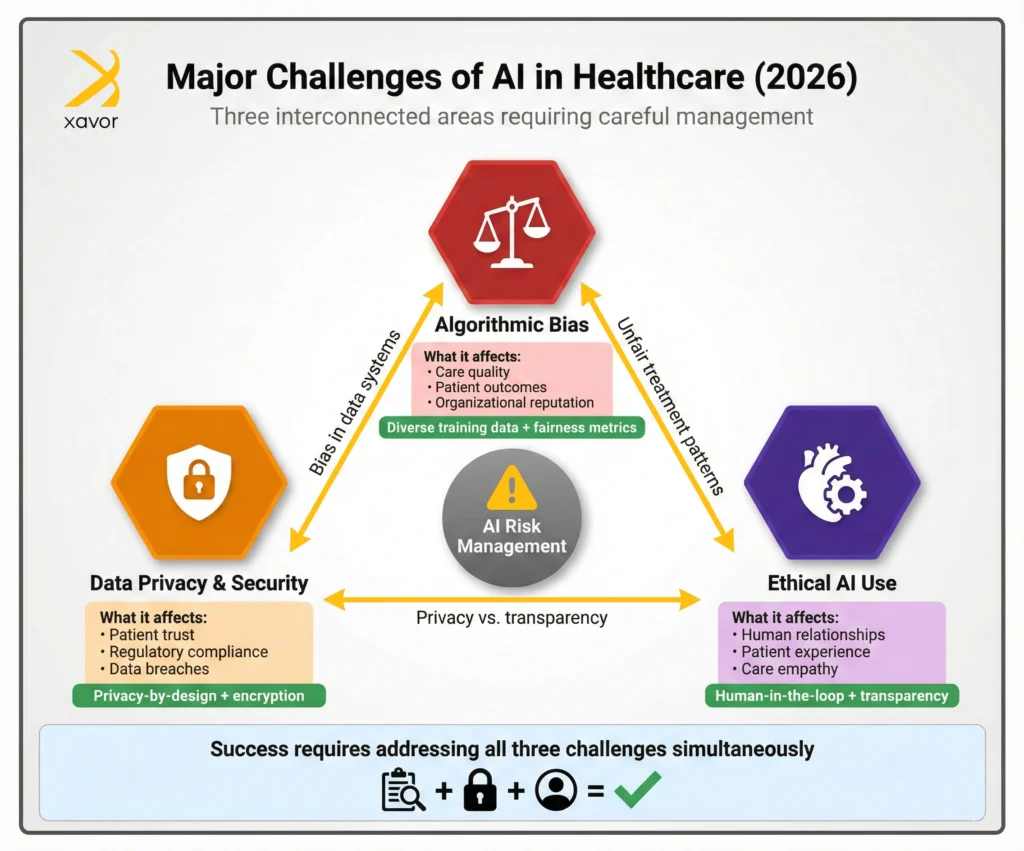
TL; DR
| Challenge | What it affects? | Solution |
| Algorithmic bias | Care quality Patient outcomes Organizational reputation | Use diverse and representative training data. Apply fairness metrics and audit models before and after deployment, while continuously monitoring outcomes. |
| Data privacy and security | Patient trust Regulatory compliance Organizational reputation | Collect only necessary data, anonymize and secure it. Keep data local when possible, strengthen cybersecurity controls, and take patients in confidence. |
| Ethical AI use in healthcare | Clinician-patient relationship Patient experience Care quality Long-term AI use | Use AI to augment human workers. Keep clinicians in the decision loop and ensure transparency and explainability. Prioritize workflows that prioritize empathy and patient experience over efficiency alone |
Historically, the healthcare industry has been slow to adopt new technology. And one major reason for that is the sensitive nature of the industry. IBM’s training guide in the 70s still rings true that, “A computer can never be held accountable, therefore a computer must never make a management decision.” That is more pertinent for the healthcare industry than any other field because you’re accountable for human lives.
There are certain risks of AI in healthcare that need to be addressed for AI in healthcare to become truly viable.
1. Algorithmic bias
Unfortunately, the history of healthcare is tainted with bias and even discrimination against certain groups or people. The Tuskegee syphilis study is quite infamous in this regard because it shows that human biases don’t even spare a noble profession like healthcare.
These biases can creep into AI algorithms because they are trained on massive data generated by none other than humans.
Algorithmic bias can lead to AI systems making unfair decisions that disadvantage certain groups, often because they learn from historical data that already contains social inequalities or because designers choose flawed models. For example, a cancer detection algorithm that misses tumors on darker skin can put someone’s life in jeopardy. These biases don’t just harm people but also erode trust and can expose organizations to legal and regulatory penalties.
Reducing bias requires more than just better code. Technically, teams need diverse training data, fairness metrics, and bias-testing tools to spot unequal outcomes early. Organizationally, models must be audited before and after deployment, with results monitored across different groups and documented clearly.
2. Data privacy and security
Never hide anything from your lawyer and doctor. This adage is as true as it gets, and certainly many people live by it. Therefore, healthcare data is highly sensitive, and any breach of patients’ electronic health records (EHRs) can expose patients’ confidential data to malicious actors.
Training and running AI systems require healthcare organizations to collect sensitive medical records. Without strong controls, this can lead to an increased risk of data leaks or cyberattacks. AI systems also have some structural vulnerabilities, like the lethal trifecta, which makes them prone to threats like prompt injections. As AI systems become more data-hungry, the relationship between artificial intelligence and big data becomes harder to separate. Therefore, poorly secured patient data used for AI training can unintentionally expose deeply personal information.
To mitigate security concerns, AI in healthcare must follow a privacy-by-design approach, which means:
- Collecting only necessary data, anonymizing it, and keeping data local whenever possible.
Another rising trend to incorporate AI solutions in healthcare is giving patients control of their own medical records. Instead of data being scattered across hospitals and systems, patients can collect, organize, and manage their complete medical history in one place and decide how it’s shared. This makes health records easier to use and gives patients more control over their own data.
3. Ethical AI use in healthcare
“Nursing is an art: and if it is to be made an art, it requires an exclusive devotion as hard a preparation as any painter’s or sculptor’s work… It is one of the Fine Arts: I had almost said, the finest of Fine Arts.”, said Florence Nightingale. She beautifully captures the essence of healthcare, which is more than accurate diagnoses or efficient workflows. It is fundamentally about human relationships.
Trust, empathy, and understanding often influence outcomes as much as clinical precision. Relying too much on AI in healthcare can make patients begin to feel processed rather than cared for. If clinicians rely heavily on AI solutions in healthcare, patient interactions may become shorter, more transactional, and more protocol-driven. Over time, this can erode empathy and make patients feel unseen or unheard, especially those with complex, chronic, or poorly understood conditions.
The solution to this risk of AI in healthcare is to support, not replace, human relationships in healthcare. AI should handle administrative and analytical tasks, so clinicians have more time and attention for patients, while final decisions remain firmly in human hands. Systems must be transparent and explainable, and workflows should prioritize empathy and patient experience over speed alone.
When designed around human values and accountability, AI in healthcare can create more space for compassion instead of eroding it.
Conclusion
You can have a thousand problems in life, but when you have a health problem, you only have one. Access to healthcare is a right, not a privilege, according to the WHO, leading human rights organizations, and the UN. Yet millions of people around the world are still denied timely, affordable, and quality care, which is an indictment for us as a global community.
This gap is to a great extent caused by strained systems, fragmented data, limited workforce capacity, and slow decision-making. AI in healthcare, if used with care and responsibility, offers a way to ease these pressures. It can help healthcare systems reach more people, detect illness earlier, support clinicians more effectively, and shift care from reaction to prevention.
But technology alone will not fix healthcare. The real impact will depend on how thoughtfully it is implemented. The future of healthcare will reflect not just what AI can do, but what we choose to do with it.
Partner with Xavor to design secure, ethical, and scalable AI solutions that improve healthcare outcomes while keeping people at the center of care. Drop us a line at [email protected] to discuss your healthcare workflows, and we’ll guide you on how AI can improve it.
Let’s turn technology into access, intelligence into equity, and innovation into real-world impact.
FAQs
In healthcare, AI can help clinicians and organizations analyze data, predict risks, and automate routine tasks. It supports earlier and more accurate diagnoses, enables personalized treatment plans, and reduces administrative burden through automation. Overall, AI in healthcare enables healthcare systems to improve their operational efficiency and provide better care quality.
There are some disadvantages of AI in healthcare if not handled properly. Risks such as algorithmic bias, data privacy and security, and over-reliance on AI may negatively impact patient outcomes. Without strong governance and regulation, AI systems can also introduce ethical, legal, and compliance risks for healthcare organizations.
Generative AI is a branch of AI that can generate human-like content, such as text, images, or videos. Generative AI in healthcare can create new content, such as clinical notes, summaries, reports, images, or treatment insights. It learns patterns from large amounts of medical data to automate documentation, synthesize patient records, support clinical decision-making, and improve patient communication.

